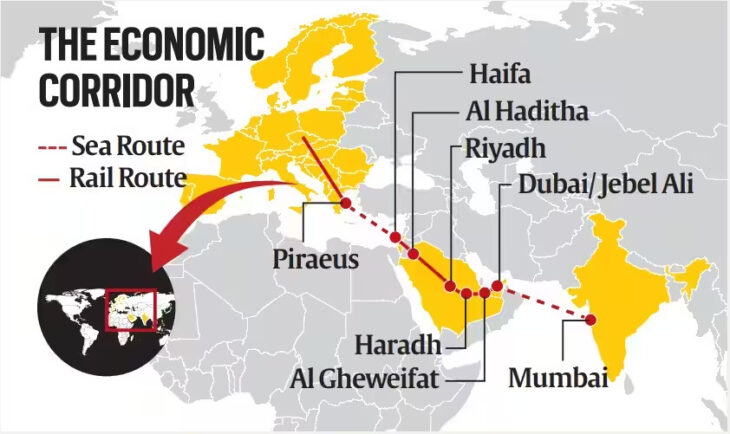
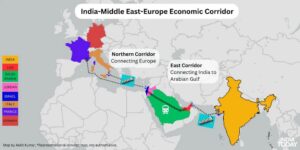
Introduction
Is India considered part of the Middle East? At first glance, this question may seem simple, but it opens up complex geopolitical, cultural, and historical issues that defy simple classification. Understanding India’s geopolitical relationships is not just an academic exercise; It is important to understand the subtle regional political, economic and cultural dynamics that shape our world. This article aims to unravel these complexities by examining the geographical, historical and political factors that define India’s position in the Middle East Through this analysis we will unravel the importance and significance of these interactions for India and her neighbors So, let us embark on this journey to remove the geopolitical boundaries and links that connect India to the Middle Eastern fabric.
Understanding Geopolitical Boundaries
Definition of Geopolitical Boundaries
Geopolitical boundaries are invisible lines that define the political and geographical limits between countries, regions, and territories. These boundaries are often based on historical claims, natural features, and legal agreements.
Discussion on How Geopolitical Boundaries Are Defined
Geopolitical boundaries are determined through:
- Treaties and international agreements.
- Natural landmarks such as rivers, mountains, and oceans.
- Historical claims and conflicts.
- Administrative decisions and legal frameworks.
Explanation of Why Defining India’s Location Is Important for Geopolitics
Understanding where India falls on the geopolitical map is crucial for several reasons:
- It influences India’s diplomatic relations and strategic partnerships.
- It affects trade routes, economic policies, and regional security.
- It shapes cultural exchanges and historical ties with neighboring regions.
Historical context
A brief overview of India’s historical relations with the Middle East
India and the Middle East share a rich tapestry of historical ties dating back thousands of years. These contacts were fostered through trade, culture and migration, and had a lasting impact on both communities.
Examining ancient trading methods and cultural change
- The Silk Road and Spice Route facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas and technology.
- These roads connected ancient Indian civilization with the Middle East, contributing to cultural and economic exchange.
- The spread of religions and philosophies, such as Buddhism and Islam, reflects the deep cultural ties that are strengthened through these ancient contacts.
The impact of colonialism and imperialism on the borders of the region
- The borders of modern-day India and the Middle East were largely shaped by colonial powers.
- British and French settlers in particular have redrawn borders, affecting geopolitics regardless of historical and cultural ties.
Political and economic relations
A study of the political and economic relations of India and the Middle East
India’s relationship with the Middle East is complex, shaped by a mixture of historical ties, economic interests and geopolitical strategies.
An overview of government relations and trade agreements
- India maintains strong diplomatic relations with several Middle Eastern countries, reflected in high-level tourism and strategic partnerships.
- Trade agreements emphasize mutual economic interests focusing on energy, technology and infrastructure.
The impact of India’s foreign policy on its relations with the Middle East
- India’s foreign policy emphasizes non-alignment, strategic liberalism and economic cooperation, which affects the approach to Middle East relations.
- Efforts to balance relations with rival powers in the region reflect India’s strategic diplomatic strategy.
- India’s growing energy needs and role as a key supplier of oil and gas to the Middle East underscore the importance of these geopolitical relationships.
Cultural and social relations
The rich tapestry of cultural and social ties between India and the Middle East is a testament to centuries of interaction. These ties are deeply embedded in the fabric of both countries, encompassing religion, language, traditions, and more.
Analysis of cultural change and shared heritage
- Historical trade routes such as the Silk Road served as routes not only for trade but also for cultural exchange, spreading art, philosophy and religious beliefs
- The shared architectural and musical traditions reflect the deep cultural imprint left by these exchanges in both places.
Religious, linguistic and traditional influences
- The spread of Islam in India and the influence of Indian spirituality in the Middle East are examples of profound religious change.
- Many Indian languages were heavily influenced by Arabic and Persian, imbuing them with a common linguistic heritage.
- Culinary traditions, with similar spices and cooking techniques, also reflect a shared cultural palate.
Case studies or examples of cultural relationships
- The Mughal Empire with its Persian influences in architecture, language and administration stands as a great example of this cultural integration.
- Popular Bollywood films and a shared love of cricket in the Middle East further highlight contemporary cultural connections.
Economic Impact
India’s economic footprint in the Middle East is marked by robust trade relations, investments, and a mutual interest in sustainable development and technology exchange.
Analysis of India’s Economic Presence in the Middle East
- India is one of the largest trading partners for several Middle Eastern countries, emphasizing the region’s importance to India’s economy.
Examination of Trade Routes, Imports, and Exports
- Historical trade routes have evolved into modern shipping lanes and air routes, facilitating the movement of goods such as oil, textiles, and technology.
- Key imports from the Middle East to India include crude oil and natural gas, whereas India exports machinery, chemicals, and textiles to the Middle East.
Discussion on Investment Opportunities and Economic Partnerships
- The Middle East’s investment in India’s technology and energy sectors highlights the growing economic synergies.
- Bilateral agreements aimed at enhancing trade, investment, and technological cooperation are setting the stage for a more interconnected economic future.
Energy Relations
The cornerstone of India-Middle East relations lies in the energy sector, with India’s growing economy heavily dependent on Middle Eastern oil and gas.
Exploration of India’s Energy Imports from the Middle East
- The Middle East accounts for a significant portion of India’s crude oil and natural gas imports, making it crucial for India’s energy security.
Analysis of Energy Security Concerns and Strategic Partnerships
- With increasing energy demands, India views its relationship with Middle Eastern countries as strategic to ensuring a stable energy supply.
- Collaborative ventures and long-term contracts are part of India’s approach to securing its energy needs while fostering good diplomatic relations.
Impact of Energy Diplomacy on India-Middle East Relations
- Energy diplomacy has not only strengthened economic ties but also led to greater political and strategic collaboration.
- Joint ventures in exploration and renewable energy projects are emblematic of the forward-looking approach both regions are taking towards energy security and sustainability.
Geopolitical Challenges
India faces a unique set of geopolitical challenges in the Middle East, a region characterized by its strategic importance and complex political landscape.
Identification of Geopolitical Challenges Facing India in the Middle East
- Navigating the Sunni-Shia divide and its impact on regional politics.
- Balancing relations with Israel and Palestine.
- Dealing with the influence of external powers like the US, Russia, and China.
Discussion on Regional Rivalries and Conflicts
- India’s approach to managing its ties with rival powers, such as Saudi Arabia and Iran.
- The impact of conflicts in Syria, Yemen, and Libya on India’s foreign policy.
Analysis of India’s Strategies to Navigate Geopolitical Complexities
- Diplomatic engagement: India employs a policy of multi-alignment, engaging with all parties to maintain stability.
- Economic partnerships: Leveraging economic ties to build goodwill and mitigate tensions.
- Strategic neutrality: Avoiding entanglement in regional conflicts while protecting its interests.
Cultural Diplomacy
India’s cultural diplomacy in the Middle East plays a crucial role in strengthening bilateral ties and promoting mutual understanding.
Examination of India’s Cultural Diplomacy Initiatives in the Middle East
- Hosting cultural festivals and art exhibitions.
- Facilitating Bollywood film screenings and music concerts.
- Establishing Indian cultural centers in Middle Eastern countries.
Analysis of Soft Power Influence Through Bollywood, Music, and Arts
- Bollywood movies as a bridge between Indian and Middle Eastern societies.
- The popularity of Indian music and dance forms.
- The role of Indian cuisine in cultural exchange.
Discussion on the Role of Education and Cultural Exchanges in Fostering Mutual Understanding
- Scholarship programs for Middle Eastern students in India.
- Academic collaborations between Indian and Middle Eastern universities.
- Cultural exchange programs promoting people-to-people ties.
Regional Security Dynamics
India’s engagement with the Middle East has significant implications for regional security dynamics.
Discussion on How India’s Presence in the Middle East Affects Regional Security
- India’s economic and military investments contribute to the region’s stability.
- The balancing act between major Middle Eastern powers and India’s strategic interests.
Analysis of India’s Involvement in Regional Conflicts or Peacekeeping Efforts
- India’s role in diplomatic initiatives to resolve conflicts.
- Contributions to UN peacekeeping operations in the Middle East.
Examination of Defense Partnerships and Military Cooperation
- Bilateral defense agreements with Middle Eastern countries.
- Joint military exercises and arms trade.
- Cooperation in counter-terrorism efforts and intelligence sharing.
Future Prospects
The future of India-Middle East relations appears poised for significant developments, shaped by both challenges and opportunities.
- Emerging Trends and Challenges: The shift towards renewable energy sources, digital transformation in trade, and geopolitical shifts in the Middle East pose challenges and opportunities for India.
- Potential Areas for Collaboration and Growth: Energy security, technology transfer, and counter-terrorism efforts stand out as key areas for deepened cooperation.
conclusion
This analysis of relations between India and the Middle East highlights a dynamic and multifaceted interaction. From ancient trade routes to modern geopolitical strategies, the relationship between India and the Middle East is historical and evolving. These case insights underscore the importance of ongoing dialogue, mutual respect, and collaborative efforts in navigating the challenges of this relationship and encourage policymakers, students, and consumers role encourages greater exploration and engagement with these issues, fostering deeper understanding and promoting regional development and stability.